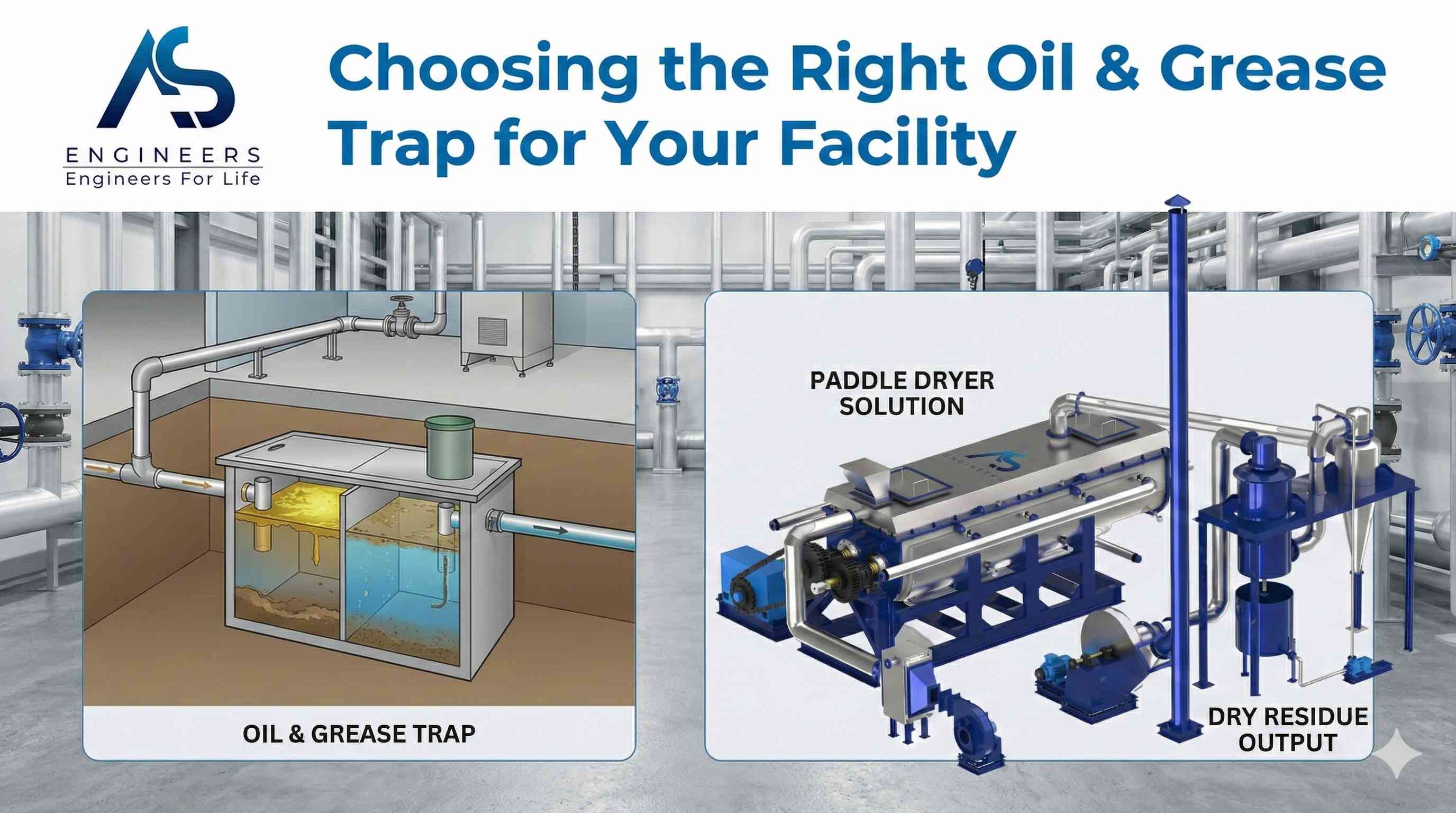
If you manage an industrial facility, commercial kitchen, or ETO plant, you know that handling wastewater is a major responsibility. Fats, oils, and grease (FOG) can cause serious problems, from clogged pipes to non-compliant discharge. Choosing the right equipment for oil removal is not just about following rules; it’s about protecting your infrastructure and the environment. An effective oil and grease management system is a critical component of any modern wastewater treatment plan, ensuring your operations run smoothly and efficiently.
Table of contents
- Key Highlights
- Understanding Oil & Grease Traps and Oil Skimmers
- Types of Oil & Grease Traps for Industrial Facilities
- Factors to Consider When Selecting Oil & Grease Removal Systems
- Benefits of Using Oil Skimmers in Industrial Wastewater
- Importance of Oil & Grease Traps in ETO Plants and Commercial Kitchens
- Paddle Dryer: The Advanced Solution for Sludge Drying
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Conclusion
Key Highlights
Here are the key takeaways from our guide on choosing the right oil and grease trap:
- Effective oil removal is essential for maintaining efficient wastewater treatment systems.
- Oil and grease traps work by separating less dense oils from water based on specific gravity.
- Integrating an oil skimmer automates the removal process, improving the efficiency of your sewage treatment plant.
- Facilities in the food processing industry must manage fats, oils, and grease to prevent drain blockages.
- Proper oil skimming and sludge management reduce environmental impact and ensure regulatory compliance.
- Advanced solutions like paddle dryers offer the best method for sludge disposal.
Understanding Oil & Grease Traps and Oil Skimmers
At first glance, oil and grease traps and oil skimmers might seem to do the same job, but they are distinct tools in the world of wastewater treatment. An oil & grease trap is a plumbing device designed to intercept FOG before it enters a wastewater disposal system.
An oil skimmer, on the other hand, is a mechanical device that actively removes floating oil from the surface of the water. When used together, they create a powerful system that significantly improves water quality and protects your drainage network. Let’s explore how each component works and what makes them different.
How Oil & Grease Traps Function in Wastewater Treatment
An oil and grease trap, also known as a grease interceptor, is essentially a holding tank that slows down the flow of wastewater from your facility. This simple but effective oil water separator is a crucial first step in wastewater treatment. Its design is based on a fundamental principle of physics: oil and grease are less dense than water.
As wastewater enters the trap, the flow rate decreases, giving the FOG time to naturally float to the surface. Heavier solids, like food particles, sink to the bottom. In the middle, cleaner water remains, which is then allowed to exit the trap and flow into the sewer system or a sewage treatment plant.
Over time, a layer of grease accumulates at the top of the trap. In a basic setup, this layer must be manually cleaned out. However, when paired with an oil skimmer, the removal process becomes automated. The skimmer continuously removes the floating oil, keeping the trap working efficiently and preventing overflows.
Key Differences Between Oil & Grease Traps and Oil Skimmers
While both devices are designed for oil removal, their methods are quite different. An oil trap is a passive system that relies on gravity to separate oil from water. It’s a receptacle that captures and holds grease. In contrast, a grease skimmer is an active machine that physically removes the captured grease from the water’s surface. Think of the trap as the container and the skimmer as the tool that empties it.
This distinction is important when deciding on a solution. A simple trap may be enough for a very small operation, but most industrial and commercial facilities benefit from the automated efficiency of an integrated oil skimming system. This combination ensures consistent performance and reduces manual labor.
Here’s a simple breakdown of the main differences:
| Feature | Oil & Grease Trap | Oil Skimmer |
|---|---|---|
| Function | Passively intercepts and holds FOG. | Actively removes FOG from the water surface. |
| Mechanism | Uses baffles and gravity separation. | Uses a moving element (belt, drum, tube) to attract oil. |
| Operation | Continuous passive collection. | Mechanical, automated removal. |
| Maintenance | Requires periodic manual clean-outs. | Requires minimal routine maintenance but automates removal. |
Types of Oil & Grease Traps for Industrial Facilities
When it comes to outfitting your facility, you have a couple of primary choices for oil and grease traps. The main distinction lies in how the collected oil is removed. Your selection will depend on the volume of wastewater you generate, the type of FOG, and your operational capacity.
For many industrial applications, the choice is between a basic, conventional trap and a more advanced unit that includes an integrated oil skimmer. Both serve as an oil water separator, but their efficiency and maintenance needs differ significantly, impacting wastewater treatment plants downstream.
Conventional Traps and Their Applications
A conventional trap is the most basic type of grease interceptor. It is a simple tank, usually installed underground or under a sink, that wastewater flows through. Inside, baffles slow the water, allowing grease to float and solid waste, like food solids, to settle at the bottom. This design is common in small commercial kitchens and restaurants.
The primary function of a conventional trap is to prevent FOG from entering and clogging the main sewer lines. It’s an effective, low-cost solution for managing kitchen wastewater at a smaller scale. These traps work entirely on gravity and have no moving parts, making them easy to install.
However, their main drawback is maintenance. As grease and food solids accumulate, the trap must be manually pumped out on a regular basis. If not cleaned frequently enough, it can become ineffective, leading to foul odors and potential blockages.
Oil & Grease Traps with Integrated Oil Skimmers
For a more efficient and automated solution, consider an oil and grease trap with an integrated grease skimmer. This system combines the passive separation of a trap with the active removal of a skimmer. The skimmer continuously pulls the collected oil and grease off the water’s surface, depositing it into a separate collection bin.
The most common type for this application is the belt skimmer. An oil skimmer belt, typically made of a material that attracts oil (oleophilic), rotates through the grease layer. The oil sticks to the belt and is then scraped off by wiper blades into a trough. This constant removal prevents the trap from filling up, ensuring it operates at peak efficiency with minimal manual intervention.
While belt skimmers are popular, other types like drum or tube skimmers can also be effective. The best choice depends on the specific type and viscosity of the oil you’re dealing with. For most food-related grease and industrial oils, a belt-type oil skimmer provides reliable, low-maintenance performance.
Factors to Consider When Selecting Oil & Grease Removal Systems
Choosing the right system for oil removal requires careful consideration of your facility’s specific needs. A one-size-fits-all approach rarely works. You need to assess factors like the daily water flow, the concentration and type of oil and grease in your wastewater, and the physical space available for installation.
Your goal should be to find a solution that is effective, compliant with local regulations, and requires minimal maintenance to operate smoothly. Thinking about these factors upfront will help you invest in a system that serves you well for years to come.
Choosing the Right Oil Skimmer for Your Plant Needs
When you’re ready to select an oil skimmer, diving into the details is key. The effectiveness of your oil skimming operation depends on matching the equipment to your specific wastewater characteristics. Different skimmers, such as belt skimmers, tube skimmers, or weir skimmers, have unique strengths.
Consider the nature of the oil. Is it thick and viscous, or light and free-floating? Some skimmers handle thick greases better, while others excel at removing thin sheens of oil. Also, think about the presence of detergents or other chemicals in your wastewater, as some surfactants can affect how well oil adheres to certain skimmer materials.
To make the best choice, evaluate the following:
- Oil Type and Viscosity: Match the skimmer’s material and design to the kind of oil you need to remove.
- Flow Rate: Ensure the skimmer can handle your facility’s volume of wastewater.
- Debris: If your wastewater contains solids or trash, you’ll need a skimmer designed to operate without clogging.
- Operating Environment: Consider factors like water temperature and chemical composition.
Benefits of Using Oil Skimmers in Industrial Wastewater
Integrating an oil skimmer into your wastewater management system offers significant advantages. Beyond just preventing pipe clogs, these devices play a crucial role in improving the overall efficiency and sustainability of your industrial applications. They help you meet environmental regulations and can even create new opportunities for your business.
By effectively removing FOG at the source, you reduce the burden on downstream treatment processes. This leads to cleaner treated wastewater, lowers your operational costs, and minimizes your environmental impact. It also opens the door to water recycling and other green initiatives.
Increased Efficiency of Sludge Management
Yes, oil skimmers absolutely improve the efficiency of sewage treatment plants. When oil and grease enter a treatment facility, they interfere with the biological processes used to break down waste. FOG can clog equipment and reduce the effectiveness of aeration systems, leading to higher operational costs and lower-quality effluent. By removing oil at the source with a skimmer, you lighten the load on your entire system.
This pre-treatment step results in a cleaner waste stream reaching the plant, which makes every subsequent stage of treatment more efficient. A significant benefit is the reduction in the volume and toxicity of the final sludge. Effective sludge management is a major challenge for many industries, and skimmers are a key part of the solution.
For facilities aiming for zero liquid discharge, managing this sludge is the final hurdle. Using advanced technology like a paddle dryer to dewater and process the sludge makes disposal or reuse far more manageable and cost-effective.
Opportunities for Recycling and Reuse of Collected Oil & Grease
The oil and grease captured by your skimmer don’t have to be just waste. In fact, this collected waste oil can become a valuable resource. With the growing focus on environmental protection and the circular economy, many industries are finding innovative ways to recycle and reuse FOG. This not only prevents waste from ending up in landfills but can also create a new revenue stream.
Whether you’re collecting animal fats, vegetable oils, or petroleum-based lubricants, there may be a recycling opportunity available. This approach supports sustainability goals and demonstrates corporate responsibility.
Here are a few common recycling and reuse pathways:
- Biodiesel Production: Used cooking oils and animal fats are excellent feedstocks for producing biodiesel.
- Rendering: Animal fats can be rendered down and used in products like soap, animal feed, and cosmetics.
- Energy Generation: Some facilities use collected FOG as a fuel source for boilers or other energy systems.
- Industrial Products: Certain waste oils can be re-processed for use in industrial lubricants or other chemical products.
Importance of Oil & Grease Traps in ETO Plants and Commercial Kitchens
For certain industries, oil and grease traps aren’t just a good idea—they are absolutely essential. In commercial kitchens and across the food processing sector, the high volume of fats, oils, and grease can quickly overwhelm a drainage system, leading to costly blockages and backups. Similarly, ETO plants must manage their effluent carefully to prevent harmful substances from entering public sewers.
In these environments, a properly functioning oil and grease trap is the first line of defense, protecting both your facility’s plumbing and the municipal wastewater infrastructure.
Regulatory and Industry Standards in India
In India, the installation and maintenance of oil and grease traps are governed by specific regulations and standards. These rules are enforced by local municipal corporations and state pollution control boards to protect public health and the environment. The primary goal is to prevent FOG from entering the public sewer system, where it can cause blockages, sanitary sewer overflows, and damage to wastewater treatment facilities.
Commercial establishments like restaurants, hotels, and food processing plants are typically required by law to install and maintain grease interceptors. The standards often specify the required size and type of trap based on the facility’s wastewater output. Failure to comply with these regulations can result in significant fines and even the suspension of business operations.
These rules ensure that all businesses do their part to maintain the integrity of the water infrastructure. By adhering to these standards, you not only avoid penalties but also contribute to better overall water quality in your community.
Typical Maintenance Schedules and Best Practices
Consistent maintenance is key to keeping your oil and grease removal system working effectively. How often you need to perform maintenance depends heavily on the volume and type of waste your facility produces. A busy restaurant may need daily checks, while some industrial applications might require less frequent inspection.
For systems with an integrated oil skimmer, the need for manual clean-outs is drastically reduced, but routine checks are still important. Regular inspection ensures the skimmer is operating correctly and that the trap is free of excessive solid waste. Establishing a clear maintenance schedule is one of the most important best practices you can adopt.
To ensure long-term performance and minimal maintenance issues, follow these tips:
- Regular Inspection: Visually inspect the trap and skimmer daily or weekly to check for proper function and buildup.
- Scrape Plates: Scrape food solids from plates and cookware before washing to reduce the load on the trap.
- Keep a Log: Maintain a log of all cleaning and maintenance activities for regulatory compliance.
- Professional Servicing: Schedule professional pumping and cleaning of the trap as needed to remove settled solids.
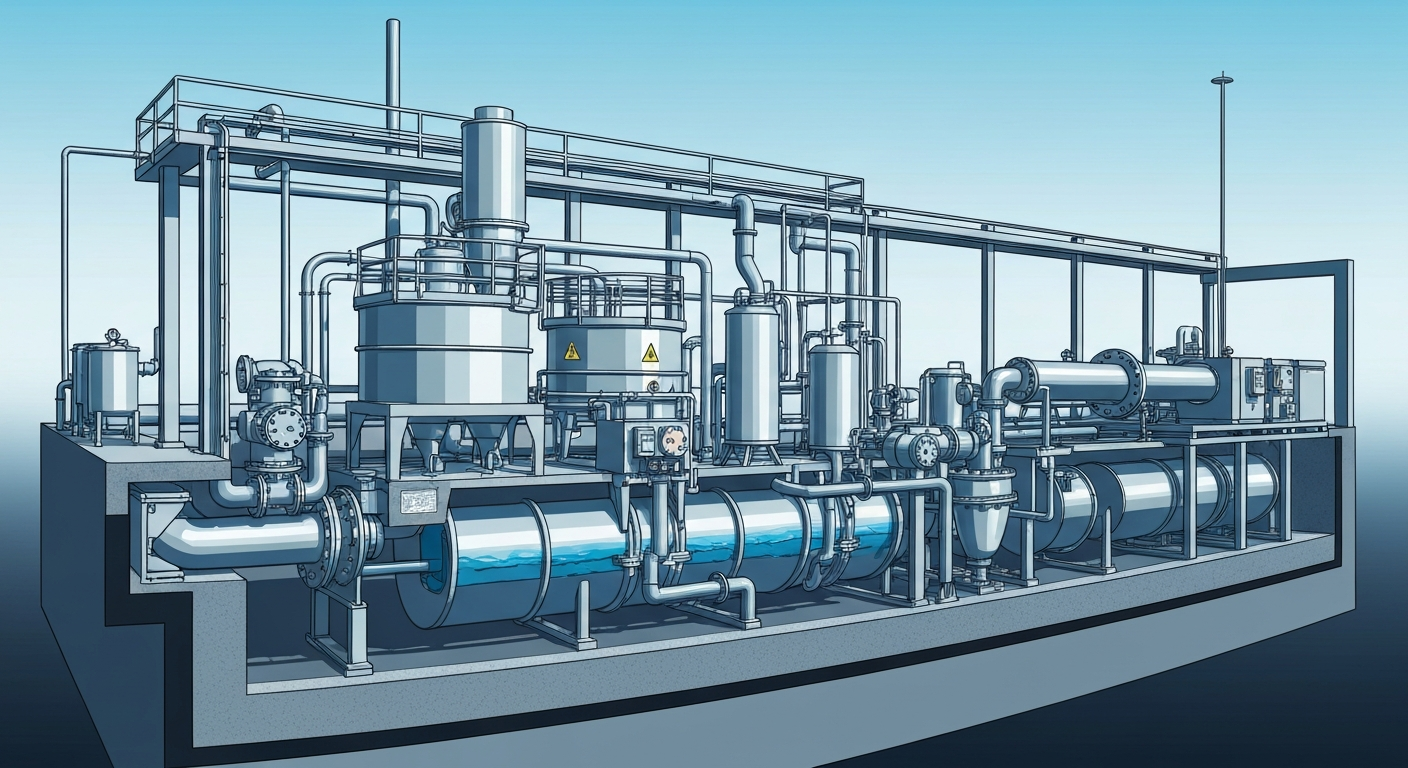
Paddle Dryer: The Advanced Solution for Sludge Drying
After you’ve successfully separated oil and solids from your wastewater, you’re left with sludge. Managing this sludge is often the most challenging and expensive part of the entire treatment process. Traditional sludge disposal methods can be costly and environmentally problematic. This is where advanced solutions like the paddle dryer come into play, offering a far more efficient and sustainable approach.

A paddle dryer is an industrial machine designed to dramatically reduce the moisture content and volume of sludge. By heating the sludge indirectly through rotating, wedge-shaped paddles, it evaporates the water, leaving a dry, manageable solid. This technology is a game-changer for facilities seeking efficient sludge disposal and further treatment options, transforming a difficult waste product into a potentially useful material.
Why Paddle Dryers are Ideal for Sludge Disposal
Paddle dryers are considered the best solution for sludge disposal for several key reasons. Their high thermal efficiency means they use less energy to remove water compared to direct drying methods, significantly lowering your operational costs. The enclosed system also contains odors and prevents dust emissions, making the workplace safer and cleaner.
The process transforms wet, heavy sludge into a dry, granular powder. This reduces its volume by up to 90%, which drastically cuts down on transportation and disposal costs. For facilities striving for zero liquid discharge, a paddle dryer is an indispensable tool. It provides a reliable and effective way to handle the final solid waste stream.
By making sludge disposal so efficient, the paddle dryer closes the loop on wastewater treatment. It ensures that every part of the waste management process is optimized, from initial oil skimming to the final handling of solids, making it the most advanced and practical solution on the market.
AS Engineers – Leading Paddle Sludge Dryer Manufacturer
When you need the absolute best solution for sludge management, look no further than AS Engineers. As the leading paddle sludge dryer manufacturer, we specialize in providing advanced solutions that are engineered for maximum efficiency and reliability. While other companies like Ventilair Engineers may be a supplier of effluent treatment components, our focus and expertise are dedicated to perfecting sludge drying technology.
Our paddle sludge dryer systems are designed to handle the toughest industrial sludges, including those from ETO plants. We understand the challenges of sludge disposal and have developed machines that deliver unparalleled performance, drastically reducing waste volume and disposal costs. Choosing AS Engineers means investing in a durable, high-performance asset for your facility.
Trust the specialists at AS Engineers to provide you with a sludge dryer that is not just a piece of equipment, but a complete, advanced solution for your waste management needs. We are committed to helping you achieve your operational and environmental goals with superior technology and expert support.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can oil and grease collected by skimmers be reused or recycled?
Yes, absolutely. The waste oil collected after oil removal can often be recycled. Depending on its type, it can be converted into biodiesel, used in rendering processes, or re-processed for industrial applications. This recycling approach supports environmental protection and turns a waste product into a potential resource.
How often should oil & grease traps be maintained in industrial settings?
Maintenance frequency varies based on the industrial application and the amount of FOG generated. A system with an integrated skimmer requires minimal maintenance, but regular inspection is crucial. A good practice is to perform weekly checks and schedule professional cleaning based on the rate of solids accumulation.
Are oil & grease traps mandatory for commercial kitchens and food processing plants?
Yes, in most regions, grease interceptors are mandatory for commercial kitchens and food processing facilities. Local regulations require these businesses to prevent FOG from entering the public sewage treatment plant. Compliance is essential to avoid fines and protect the municipal wastewater infrastructure from damage and blockages.
What factors should I consider when selecting an oil and grease trap for my facility?
When selecting an oil water separator, consider your facility’s specific needs. Key factors include the daily water flow, the type and concentration of oil needing removal, available space, and local regulations. Choosing correctly ensures your drainage system is protected and your oil removal process is efficient.
How often should oil and grease traps be inspected and maintained?
Inspection and maintenance schedules depend on usage. Best practices suggest daily or weekly visual inspection to ensure proper function. Professional cleaning to remove accumulated solids and sludge should be scheduled based on how quickly the trap fills, which could be monthly or quarterly for many establishments.
Are there specific regulations or standards I need to follow when installing an oil and grease trap?
Yes, there are specific regulations and standards for installing grease traps, especially for commercial and industrial facilities. These are set by local municipalities and pollution control boards to protect the public sewer system. You must ensure your effluent treatment plant and its components meet these local codes.
What are the differences between passive and active oil and grease traps?
A passive oil & grease trap is a simple tank that uses gravity to let FOG float to the top. An active system incorporates a mechanical device, like an oil skimmer, to continuously remove the collected FOG. Active systems are more efficient and reduce the need for manual cleaning.
Conclusion
In conclusion, selecting the right oil and grease trap is essential for maintaining efficient wastewater management in your facility. Understanding the functionality and differences between various types of traps and skimmers will enable you to make informed decisions that comply with regulatory standards and best practices.
Additionally, incorporating advanced solutions like paddle dryers can greatly enhance sludge disposal processes, making them more efficient and environmentally friendly. If you’re ready to optimize your facility’s operations and ensure compliance, reach out to us for a free consultation. Let AS Engineers guide you in choosing the best solutions tailored to your needs.