Effective wastewater treatment is essential for protecting our environment and meeting regulatory standards. A key challenge in this process is removing oil and grease that contaminate water. An oil skimmer is a simple yet powerful tool designed for this exact purpose. By separating oil from water, these devices help ensure environmental compliance and improve the overall efficiency of treatment plants. This guide will compare two popular types, the belt skimmer and the disc skimmer, to help you understand which is best for your needs.
Table of contents
- Key Highlights
- Overview of Oil Skimmers in Waste Water Treatment
- What Is a Belt Skimmer?
- What Is a Disc Skimmer?
- Comparing Belt Skimmer vs. Disc Skimmer – Features & Usage
- Principles of Oil Separation (Specific Gravity, Surface Tension, and Affinity)
- Factors Affecting Oil Removal in Waste Water Treatment
- Other Types of Oil Skimmers (Drum/Barrel, Mop, Tube, Floating Suction, etc.)
- Conclusion
- Frequently Asked Questions
Key Highlights
- An oil skimmer is a crucial mechanical device for oil removal in wastewater treatment.
- The main difference between a belt skimmer and a disc skimmer lies in their collection media and applications.
- Belt skimmers are versatile and effective for various tank sizes and fluctuating water levels.
- Disc skimmers are compact and suitable for smaller tanks with consistent water levels.
- Both skimmers improve water quality and help facilities meet environmental compliance standards.
- Choosing the right oil skimmer depends on factors like oil type, tank size, and specific industrial applications.
Overview of Oil Skimmers in Waste Water Treatment
An oil skimmer is a machine that removes floating oil, grease, and other hydrocarbons from the surface of water. Since oil is lighter than water, it naturally rises, creating a layer that a skimmer can easily target. This oil removal process is vital in many industrial wastewater systems to maintain clean operations and adhere to environmental standards.
These devices work by using a moving medium—like a belt, disc, or tube—that oil adheres to. The medium then lifts the oil out of the water and carries it to a wiper system that scrapes it into a collection container. Unlike belt and disc skimmers that are typically fixed, some floating oil skimmers use a pump or suction intake that floats on the surface, making them suitable for applications with thick oil layers.
Role of Oil Skimmers in ETP and STP Plants Across India
In India, Effluent Treatment Plants (ETP) and Sewage Treatment Plants (STP) rely on effective technology to manage industrial and municipal wastewater. An oil skimmer plays a critical part in these facilities by removing floating oils and greases at an early stage. This pre-treatment step significantly reduces the load on downstream processes like biological treatment units.
By efficiently scooping oil from the water’s surface, both belt and disc skimmers prevent contamination from spreading and help the plant operate more efficiently. Their use is crucial for meeting the stringent environmental compliance standards set by regulatory bodies. Whether for a small local plant or a large industrial ETP, these skimmers are highly suitable and offer a reliable solution.
The continuous, automated oil removal provided by these skimmers ensures that the discharged water is cleaner, protecting our natural water resources. This makes them an indispensable tool for any modern industrial wastewater treatment facility looking to improve its performance and environmental footprint.
Need for Effective Sludge and Oil Removal
Effective oil removal is not just a suggestion; it’s a necessity for maintaining water quality and adhering to environmental regulations. When oil contamination is left unchecked in wastewater, it can harm aquatic life, clog pipes, and damage treatment equipment. This leads to higher maintenance costs and potential fines for non-compliance.
The presence of floating oil can also interfere with other treatment processes, reducing their overall effectiveness. The goal is to remove as much oil as possible before it has a chance to emulsify or mix further with the water. The efficiency of oil removal depends on factors like the type and thickness of the oil, water turbulence, and the specific design of the skimmer.
Ultimately, investing in an effective oil and sludge removal system protects your equipment, lowers disposal costs, and ensures your facility operates smoothly. It is a proactive step toward sustainable water management and responsible industrial practice.
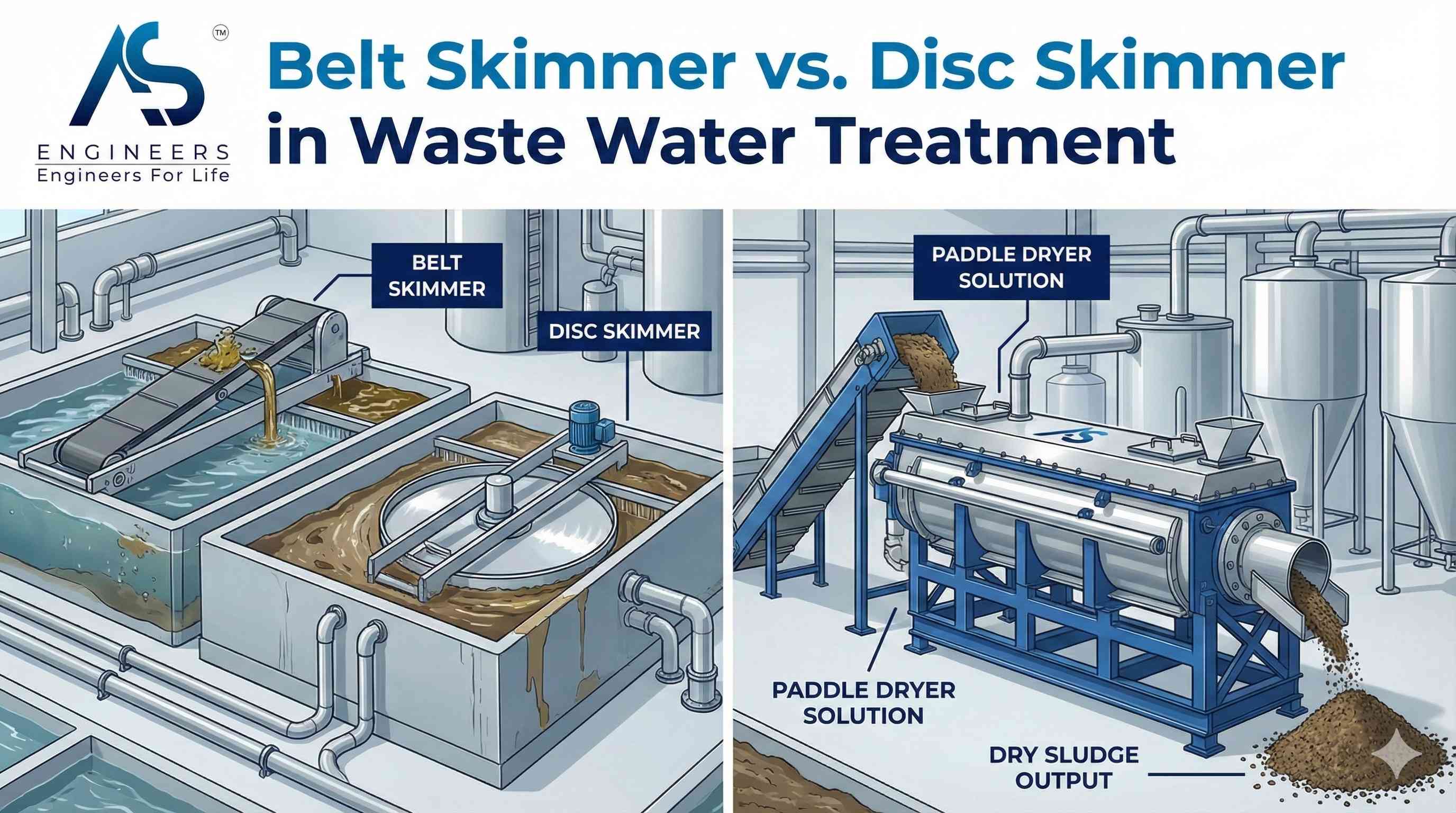
What Is a Belt Skimmer?
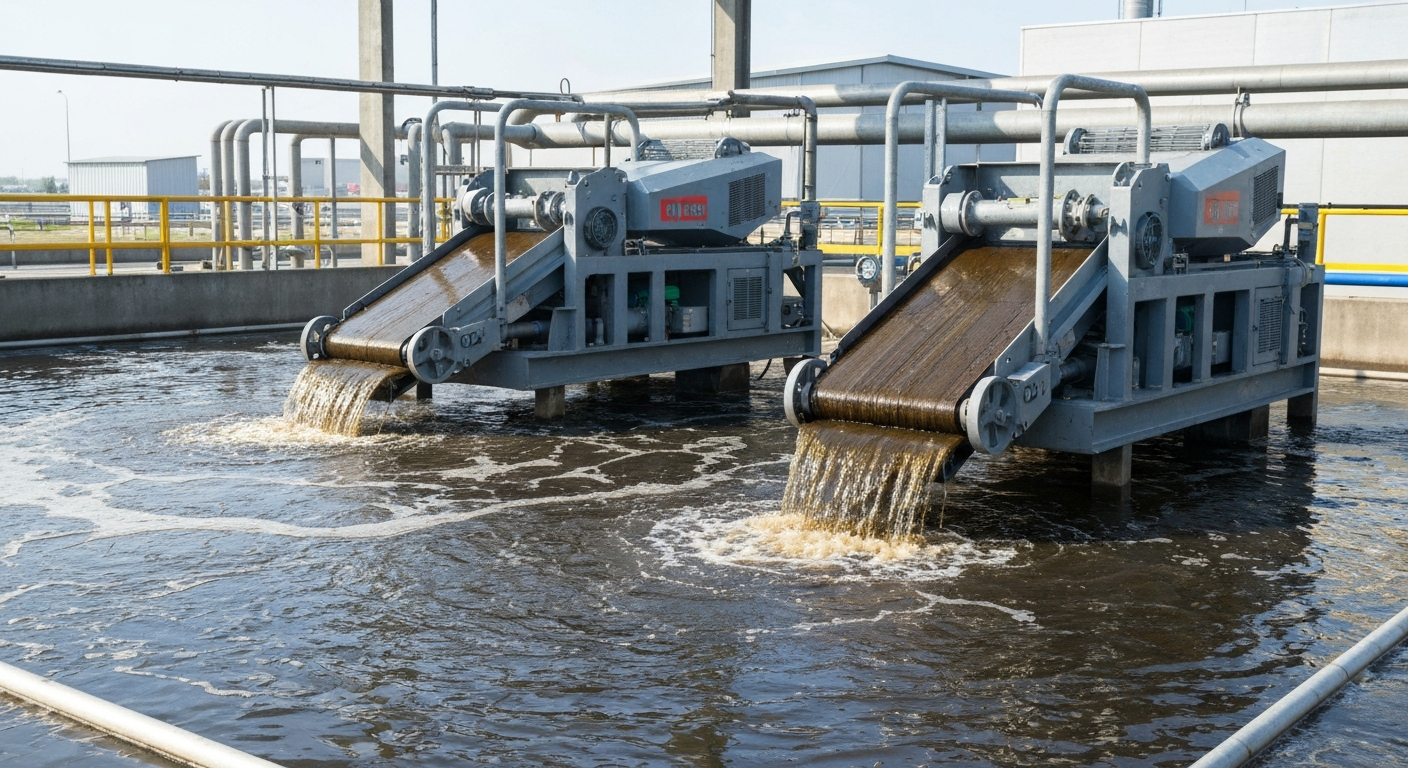
A belt skimmer is a mechanical device designed for oil skimming. It uses a continuous belt made of stainless steel or a special polymer that is lowered into a tank of water. As the belt moves, floating oil adheres to its surface, lifting it out of the water.
This industrial oil skimmer is known for its simplicity and reliability. The main difference between a belt skimmer and a disc skimmer is the medium used for collection; a belt skimmer uses a long, flat belt, which often gives it a longer reach and makes it more adaptable to fluctuating water levels. Next, we will explore how this device operates and what it is made of.
Principle of Operation and Key Components
A belt skimmer works based on the simple principles of surface tension and affinity. Oil has a natural tendency to stick to the skimmer’s belt material more readily than water does. The belt moves through the water’s surface, where it picks up the floating oil.
The oil-coated belt then travels up into the skimmer’s housing unit. Here, a set of wiper blades scrapes the oil off both sides of the belt. The recovered oil then flows into a collection tank or drum for proper disposal or recycling. This continuous cycle provides an automated and low-maintenance method for oil removal.
Key components of belt oil skimmers include:
- The Belt: Often made from durable materials like stainless steel or polymer for a long service life.
- Motor and Pulleys: A drive system that keeps the belt in constant motion.
- Wiper Blades: These scrape the oil from the belt into the collection tank.
Types of Oils Removed by Belt Skimmers
Belt oil skimmers are remarkably versatile and can efficiently remove a wide range of oils from the water’s surface. They are not limited to just one type of oil, making them suitable for many different industries. Whether you are dealing with light oils or more viscous substances, a belt skimmer can likely handle the job.
These skimmers are particularly effective at removing tramp oil from machine coolants, which helps extend coolant life and improve machining quality. In the food processing industry, they are used to remove vegetable oils and animal fats from wastewater. The ability to manage different viscosities is a key advantage.
A belt skimmer can effectively remove:
- Heavy oils and greases found in steel mills and industrial sumps.
- Tramp oil that contaminates CNC machine coolants.
- Oils and fats generated during food processing.
What Is a Disc Skimmer?
A disc skimmer is another effective tool for oil removal in industrial wastewater treatment. This disc type of oil skimmer uses a rotating disc, typically made of plastic or metal, that is partially submerged in the liquid. As the disc turns, oil from the water’s surface adheres to it.
Once the oil-coated section of the disc rotates out of the liquid, it passes by stationary wiper blades that scrape the oil off into a collection trough. Disc skimmers are often used in industrial wastewater systems where space is limited, as they have a compact design. Let’s look closer at how they work and where they are used.
Working Mechanism of Disc Skimmers
The working principle of a disc skimmer is similar to that of a belt skimmer, relying on surface tension and the affinity of oil for the disc material. A motor rotates the disc, causing its lower portion to pass through the oil layer on the water surface. The oil sticks to the disc while the water runs off.
As the disc continues to rotate, the collected oil is lifted out of the water. Wiper blades are positioned on both sides of the disc to scrape the oil off as it passes. The recovered oil is then channeled into a collection container for disposal.
This mechanism allows the disc type oil skimmer to continuously and efficiently remove oil. However, its effectiveness is often dependent on a consistent water level, as only the submerged portion of the disc can pick up oil. This makes it ideal for tanks where the fluid level does not fluctuate significantly.
Typical Applications in Industrial Wastewater Treatment
Disc skimmers are well-suited for a variety of industrial applications, particularly where space is a constraint. Their compact design makes them a great choice for smaller tanks, sumps, and parts washers where a larger belt skimmer might not fit.
You should consider using a disc skimmer instead of a belt skimmer in situations with stable water levels and limited surface area. In machine shops, they are used to remove tramp oil from the coolant in individual machine tools, helping to maintain the quality of the fluid and the parts being produced.
Some common industrial applications include:
- Parts washing tanks: To remove floating oils that can re-contaminate clean parts.
- Coolant sumps for machine tools.
- Small industrial wastewater sumps in various manufacturing facilities.
Comparing Belt Skimmer vs. Disc Skimmer – Features & Usage
When choosing between a belt skimmer and a disc skimmer, it’s important to understand their core differences in features and usage. The primary distinction is their collection medium: a belt skimmer uses a long, continuous belt, while a disc skimmer uses a rotating disc. This fundamental difference influences where and how each is best used for oil skimming.
A belt skimmer’s long reach makes it more versatile for large tanks or when the water level fluctuates. In contrast, a disc skimmer is more compact, making it ideal for tight spaces. The next sections will compare their performance and identify the best scenarios for each type.

Efficiency and Performance Parameters
The efficiency of an oil skimmer is measured by several performance parameters, including its oil recovery rate and the amount of water it picks up. Both belt and disc skimmers are designed for high recovery efficiency, but their performance can be affected differently by operating conditions. A skimmer’s pickup rate is influenced by the oil’s viscosity, the speed of the medium, and the thickness of the oil layer.
For optimal performance, you want a skimmer that maximizes oil removal while minimizing water content in the collected product. Belt skimmers often excel in applications with fluctuating water levels, as the belt can reach deeper into the tank. Disc skimmers perform best with stable liquid levels, as their pickup area is fixed by their diameter. The removal capacity is a key factor, often expressed in gallons or liters per hour.
Here is a comparison of their performance features:
| Feature | Belt Skimmer | Disc Skimmer |
|---|---|---|
| Removal Capacity | Generally higher; scalable with belt width | Good for its size, but limited by disc diameter |
| Water Level Fluctuation | Handles fluctuations well due to long reach | Less effective; requires stable water levels |
| Space Requirement | Requires more vertical space | More compact, ideal for tight spaces |
| Water Pickup | Typically very low | Also low, but can increase if not sized correctly |
Situations Best Suited for Each Type
Choosing the right skimmer depends entirely on your specific site conditions and treatment process needs. One skimmer type would be preferred over the other based on factors like tank size, accessibility, and the nature of the oil contamination.
A belt skimmer is the preferred choice in scenarios where the water level fluctuates, or you need to skim from a deep tank. Its long belt can easily adapt to changing liquid levels, ensuring consistent oil removal. They are also ideal for larger tanks or pits where a greater surface area needs to be covered.
On the other hand, a disc skimmer is better suited for:
- Small tanks or sumps with limited installation space.
- Applications where the water level is relatively constant.
- Individual machine tools or parts washers needing a compact solution.
Principles of Oil Separation (Specific Gravity, Surface Tension, and Affinity)
The success of oil skimming relies on a few basic scientific principles: specific gravity, surface tension, and affinity. Most oils have a lower specific gravity than water, which means they are less dense. This is why oil naturally separates and floats on the liquid surface, creating a distinct layer that can be removed. This principle is the foundation of all surface oil separation techniques.
Surface tension and affinity also play a crucial role. Oil molecules tend to bond more tightly to each other and to the skimmer’s media (belt or disc) than they do to water. This property, known as affinity, is what allows the skimming medium to pick up oil with very little water. For example, a disc skimmer in an industrial system rotates through the water, and the oil’s affinity for the disc material causes it to cling on, allowing for efficient removal as it exits the liquid.
Factors Affecting Oil Removal in Waste Water Treatment
Several factors can affect the effectiveness of oil removal in your wastewater treatment system. The characteristics of the wastewater itself, such as its temperature and pH, can influence how well a skimmer performs. Additionally, the physical layout of your facility plays a significant role.
The tank size, shape, and the presence of turbulence on the surface of water all impact a skimmer’s ability to capture oil. For instance, a very large tank might require a skimmer with a longer reach, while a turbulent surface can make it harder for oil to be picked up. We’ll now look at these factors in more detail.

Wastewater Characteristics and Site Conditions
The effectiveness of any industrial oil skimmer is directly tied to the specific wastewater characteristics and site conditions. For instance, the viscosity of the oil matters. Thicker, heavier oils may require a more robust skimmer or even heating elements to ensure they remain fluid enough to be collected and discharged.
Water quality factors like pH and the presence of chemicals can affect the longevity of the skimmer’s components. You should choose a skimmer with materials resistant to the chemicals in your wastewater. Another key consideration is turbulence; a quiet area in the tank will allow oil to accumulate, making it easier for the skimmer to do its job.
Important site conditions to consider include:
- Tank Size and Shape: A large or irregularly shaped tank may require a skimmer with a longer reach, like a belt skimmer.
- Water Level Fluctuation: Constantly changing levels make belt skimmers a more reliable choice.
- Temperature: Extreme temperatures may require specialized materials or heaters for the skimmer.
Maintenance Needs and Longevity of Disc Skimmers and Belt Skimmers
When comparing belt and disc skimmers, maintenance needs and longevity are important considerations. Both types are generally designed for low maintenance, but their requirements can differ slightly. Regular checks and cleaning are key to ensuring a long service life for any skimmer.
Belt skimmers may require periodic tension adjustments and replacement of wiper blades and the belt itself over time. However, their simple design often translates to minimal maintenance costs. The durability of the belt material, whether it is stainless steel or a polymer, is a major factor in its longevity, especially in harsh environments like steel mills.
Disc skimmers also require wiper blade replacements and regular cleaning. Because of their more compact, contained design, they can sometimes be easier to access for service.
- Belt Skimmers: May need belt tensioning; wiper and belt replacement are the main recurring tasks.
- Disc Skimmers: Wiper blade replacement is the most common maintenance item.
- Both: Require a clean motor and drive system for optimal longevity.
Other Types of Oil Skimmers (Drum/Barrel, Mop, Tube, Floating Suction, etc.)
While belt and disc skimmers are very common, they are not the only options available for oil removal. Other types, such as drum skimmers, mop skimmers, and tube skimmers, offer different advantages depending on the application. Drum skimmers are similar to disc skimmers but use a rotating drum, giving them a higher removal capacity. Mop skimmers use a rope-like medium that is wrung out to release the oil, which is effective for viscous oils but can pick up a lot of water.
A tube oil skimmer uses a floating plastic hose that snakes across the water’s surface, making it great for shallow tanks or hard-to-reach areas. Floating suction skimmers are different because they don’t use an oleophilic (oil-attracting) medium. Instead, they use a floating intake connected to a pump to skim the oil layer from the surface. This design is best for thick oil slicks but can sometimes pull in more water compared to belt or disc types.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding the differences between belt skimmers and disc skimmers is essential for optimizing wastewater treatment processes. Each type of skimmer has its unique features, operational mechanisms, and specific applications that can significantly affect efficiency and performance in removing oil from wastewater. By evaluating your facility’s needs and characteristics, you can make an informed decision on which skimmer will provide the best results. As the leading manufacturer of paddle dryers, AS Engineers is here to support your sludge management solutions. If you have any questions or need assistance in selecting the right equipment for your treatment plant, get in touch with us today!
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the main differences between a belt skimmer and a disc skimmer in wastewater treatment?
The main difference is the collection medium. A belt skimmer uses a long, continuous belt, making it ideal for large tanks and fluctuating water levels. A disc skimmer uses a rotating disc, which is more compact and best suited for smaller tanks with stable water levels.
Are belt or disc skimmers ideal for STP and ETP plants in India?
Yes, both belt and disc skimmers are ideal for STP and ETP plants. They provide efficient and automated oil removal, helping plants meet environmental standards and improve overall treatment efficiency. A belt skimmer is great for larger tanks with fluctuating water levels, while a disc skimmer is perfect for smaller, compact applications.
How does each skimmer type affect the efficiency of oil removal?
A belt skimmer’s efficiency is consistent even with changing water levels due to its long reach. A disc skimmer’s recovery efficiency is highest when the water level is stable, ensuring the disc is optimally submerged. Both use surface tension to achieve high efficiency with low water pickup.
In what scenarios would one skimmer type be preferred over the other for wastewater treatment applications?
Prefer a belt skimmer for large tanks, deep sumps, or when the water level fluctuates. Choose a disc skimmer for small tanks, tight spaces, and applications with a consistent water level, such as parts washers or individual machine sumps, as part of your treatment process.
What are the advantages and disadvantages of using belt skimmers compared to disc skimmers?
Belt skimmers are advantageous for their versatility and reach, though they may require more space. Disc skimmers are compact and efficient in tight spots but are less effective with fluctuating water levels. Both have low maintenance costs and high operational efficiency when used in the right application.
What are the main differences between belt skimmers and disc skimmers in wastewater treatment?
The primary difference is their design for oil removal. A belt skimmer uses a long belt to lift oil from the water surface, offering greater reach. A disc skimmer uses a rotating disc, which is more compact but requires a stable water surface for effective operation.
How do operational costs compare between belt skimmers and disc skimmers?
Operational costs are generally low and comparable for both. Maintenance costs mainly involve replacing wipers and occasionally the belt or disc. Long-term costs are similar, but a mismatched application (e.g., a disc type in fluctuating water) could lead to lower efficiency and indirectly higher disposal costs.
What factors should be considered when choosing between a belt skimmer and a disc skimmer for a treatment facility?
Consider your specific site conditions: tank size and shape, water level fluctuations, available space, and required removal capacity. Also, evaluate the water quality and oil type to ensure the skimmer’s materials are compatible and its performance will be optimal for your needs.
Which type of skimmer is more effective for specific types of waste materials?
Both belt oil skimmers and disc type skimmers are effective for most free-floating waste oil. Belt skimmers might have an advantage with thicker or heavier oils due to a larger surface area and robust build, while both handle lighter oils and tramp oil very well in their respective applications.