Oil sludge is a persistent and hazardous byproduct of the oil and petrochemical industry. This semi-solid waste, a mixture of hydrocarbons, water, and solids, presents major challenges for waste management. If not handled correctly, it can cause severe environmental damage, contaminating soil and water resources. This guide explores innovative treatment and disposal solutions that not only mitigate the environmental impact of oil sludge but also offer opportunities for resource recovery, turning a difficult waste product into something of value.
Table of contents
- Key Highlights
- Understanding Oil Sludge Formation and Types
- Environmental and Operational Challenges of Oil Sludge
- Legal Regulations and Standards Governing Oil Sludge Treatment
- Introduction of New Sludge Treatment Technologies
- Step-by-Step Overview of Oil Sludge Treatment
- Advanced Oil Sludge Drying Techniques
- Safe and Sustainable Oil Sludge Disposal Methods
- Equipment Used in Oil Sludge Treatment Plants
- Preventive Strategies for Oil Sludge Buildup
- Conclusion
- Frequently Asked Questions
Key Highlights
- Oil sludge poses a significant environmental impact, requiring advanced treatment technologies for safe management.
- The sludge drying process is crucial for reducing waste volume and preparing it for sludge disposal or resource recovery.
- Modern sludge dryers, like the Paddle Dryer, offer an efficient method for treating oil sludge and converting it into valuable material.
- Effective treatment minimizes the environmental footprint of industrial operations and helps in recovering valuable hydrocarbons.
- Proper sludge disposal methods, including incineration and reuse, are vital for sustainable waste management.
- Understanding oil sludge formation helps in implementing preventive measures and choosing the right treatment.
Understanding Oil Sludge Formation and Types

Oil sludge is the residue that forms during the extraction, transportation, and refining of crude oil. It is a complex blend of hydrocarbons, water, sediments, and various chemicals. Due to its composition, which includes organic matter and potentially hazardous substances, this type of sludge requires careful handling.
The specific characteristics of oil sludge can vary depending on its source. For instance, sludge from a crude oil tank will differ from the sludge that builds up inside an engine. Understanding these differences is key to selecting the most effective treatment method. Let’s examine how this sludge forms and the key distinctions between its types.
How Oil Sludge Forms in Industrial and Engine Systems
In industrial settings like refineries, sludge formation is a gradual process. As crude oil is stored in large tanks, heavier hydrocarbons, sediments, and water settle at the bottom. This mixture, known as refinery sludge, accumulates over time, reducing storage capacity and creating a hazardous waste that needs removal and treatment. The high water content in this sludge often makes it difficult to process.
A similar process occurs in vehicle engines, leading to engine oil sludge. Over time, engine oil degrades due to high temperatures and oxidation. Contaminants like dirt, metal particles, and partially burned fuel mix with the oil. This mixture thickens and forms a gel-like substance that can clog oil passages.
Skipping regular oil changes accelerates this sludge formation, as the oil becomes saturated with contaminants and loses its ability to lubricate and clean engine components effectively. The result is a thick, tarry deposit that can lead to poor engine performance and eventual failure.
Key Differences Between Oil Sludge and Engine Sludge
While both are forms of sludge, oil sludge from industrial processes and engine sludge from vehicles have distinct differences in their origin, composition, and impact. Understanding these distinctions is important for proper sludge removal and treatment.
Industrial oil sludge primarily originates from the storage and refining of crude oil. It accumulates in large quantities in tanks and pipelines. In contrast, engine sludge forms inside an internal combustion engine as the engine oil breaks down and collects contaminants.
Here are the key differences:
- Source: Oil sludge comes from large-scale industrial activities, while engine sludge is specific to vehicle engines.
- Composition: Industrial sludge is a mix of hydrocarbons, water, and sediment. Engine sludge contains degraded oil, metal particles, fuel byproducts, and dirt.
- Volume: Refineries and storage facilities produce tons of oil sludge, whereas an engine produces a much smaller volume.
- Impact: Industrial sludge is a major environmental hazard requiring specialized disposal. Engine sludge primarily affects engine performance and longevity.
Environmental and Operational Challenges of Oil Sludge
Oil sludge creates significant problems for both the environment and industrial operations. Classified as a hazardous waste, its disposal is costly and heavily regulated. Improper handling can lead to severe pollution, making its management a top priority for companies aiming for environmental responsibility.
Beyond its environmental impact, oil sludge also affects equipment efficiency. Buildup in tanks reduces storage capacity, while accumulation in machinery can cause blockages and failures, leading to expensive downtime and repairs. These challenges highlight the need for effective treatment solutions. We will now explore these impacts in more detail.
Impacts of Improper Oil Sludge Disposal
Improper sludge disposal can have devastating effects on the environment and human health. When waste oil and sludge are dumped without proper treatment, the toxic components can leach into the ground, contaminating soil and groundwater. This environmental pollution can harm local ecosystems for years.
The presence of heavy metals and other hazardous substances in oil sludge makes it a direct threat. Water sources can become undrinkable, and agricultural land may become unusable. These contaminants can enter the food chain, posing long-term risks to wildlife and people.
The consequences of irresponsible disposal include:
- Soil and Water Contamination: Hazardous chemicals seep into the environment.
- Air Pollution: Unsafe disposal methods like open burning can release toxic fumes.
- Harm to Wildlife: Contaminated habitats can lead to the decline of local animal and plant populations.
- Risks to Human Health: Exposure to heavy metals and toxins can cause serious health issues.

Consequences for Equipment Efficiency and Maintenance
Oil sludge buildup directly harms the performance and lifespan of industrial equipment and engines. In storage tanks, sludge accumulates at the bottom, reducing the effective storage volume and requiring costly and time-consuming cleanouts. In machinery, it can clog pipelines, filters, and pumps, restricting flow and leading to operational failures.
For engines, the consequences are equally severe. Sludge can block narrow oil passages, starving critical engine components of lubrication. This lack of oil flow leads to increased friction and heat, causing premature wear and tear on parts like bearings and camshafts. If left unaddressed, it can result in complete engine failure.
Ultimately, sludge buildup increases maintenance requirements and drives up operational costs. Frequent cleaning, repairs, and part replacements become necessary, leading to unplanned downtime and reduced productivity. Proactive management and treatment are essential to maintain equipment efficiency and control expenses.
Legal Regulations and Standards Governing Oil Sludge Treatment
The treatment and disposal of oil sludge are governed by strict environmental regulations worldwide. Because of its composition, oil sludge is typically classified as a hazardous waste, meaning its handling, transportation, and disposal must adhere to specific legal requirements. These laws are designed to prevent environmental contamination and protect public health. Regulatory bodies mandate that industries use approved treatment processes to reduce the hazardous nature of the sludge before its final disposal.
Compliance with these standards is not optional. Companies that fail to manage their oil sludge according to these rules face severe penalties, including large fines and legal action. Therefore, it is crucial for industries to invest in compliant treatment technologies and maintain thorough records of their waste management practices. Following these regulations ensures that sludge disposal is done safely and responsibly, minimizing risk and liability.
Introduction of New Sludge Treatment Technologies
As environmental standards become more stringent, the demand for more effective oil sludge treatment technologies has grown. Traditional methods like simple separation are often insufficient to meet modern requirements. In response, the industry has developed innovative techniques that offer better efficiency, higher oil recovery rates, and a smaller environmental footprint. These advanced methods aim to separate oil, water, and solids more completely.
Among the recent developments are processes like thermal treatment, solvent extraction, and ultrasonic treatment. Thermal methods use heat to evaporate water and recover oil, while solvent extraction uses chemicals to dissolve hydrocarbons from the sludge. Each of these treatment technologies offers unique advantages for processing different types of oil sludge. These advanced solutions are transforming how industries manage this challenging waste stream, turning it from a liability into a potential resource.
Step-by-Step Overview of Oil Sludge Treatment
The treatment of oil sludge is a multi-stage process designed to safely separate its three main components: oil, water, and solids. The overall goal is to maximize oil recovery for reuse, treat the water so it can be safely discharged, and process the solids for proper disposal. Effective sludge treatment methods are essential for minimizing waste and environmental harm.
This journey from hazardous waste to manageable components involves several key treatment processes. It begins with the initial sludge removal and collection and moves through various separation and purification stages. The following sections will provide a closer look at these steps, from initial stabilization to the final cleaning of tanks.

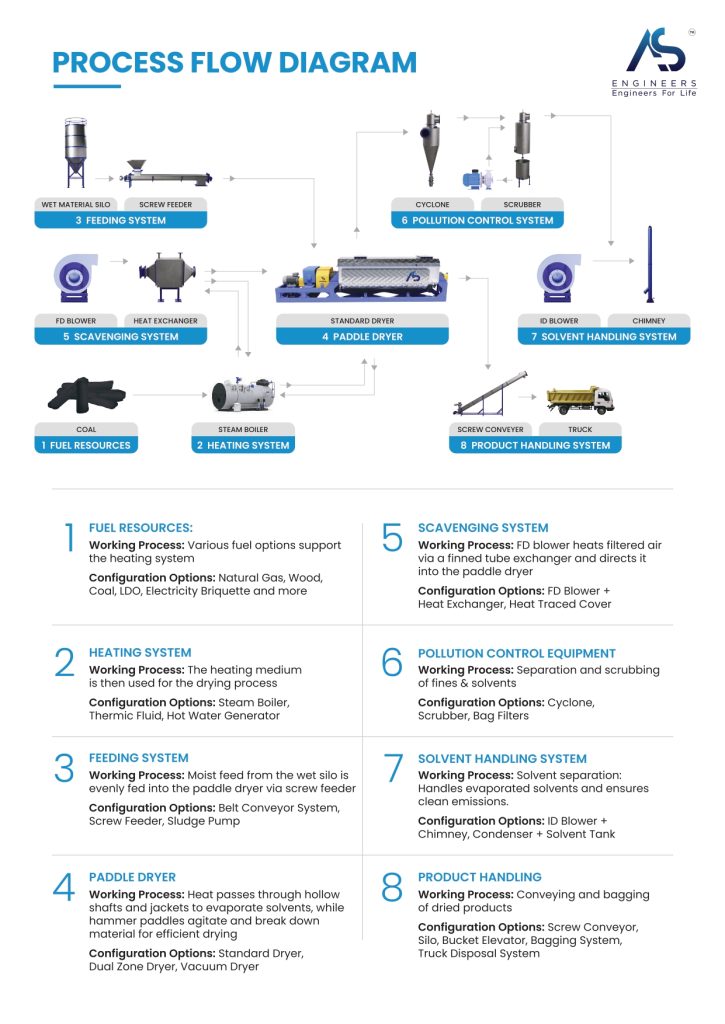
Collection, Stabilization, and Separation Processes
The first step in any oil sludge treatment method is the safe collection of the sludge from tanks or pits. Once collected, the sludge often undergoes a stabilization process. This may involve chemical treatment to break down emulsions, which are stable mixtures of oil and water that are difficult to separate. Stabilization makes the subsequent separation stages more efficient.
After stabilization, the process focuses on separating the different phases of the sludge. This is typically done using mechanical methods like centrifuges, which use high-speed rotation to separate components based on density. The goal is to isolate the oil phase from the water and solid particles as much as possible.
The separation process can be visualized as sorting the sludge into distinct layers, each requiring its own treatment path.
| Component | Description | Goal of Separation |
|---|---|---|
| Oil Phase | Recoverable hydrocarbons and residual oil. | Recover valuable oil for reuse or reprocessing. |
| Water Phase | Water mixed with dissolved salts and some organic pollutants. | Treat water for safe disposal or reuse in the facility. |
| Solid Particles | Sediment, sand, rust, and other inorganic materials. | Reduce volume and prepare for safe disposal, often in a landfill. |
Cleaning Oily Sludge from Tanks and Storage Systems
Cleaning oily sludge from large storage tanks is a critical but challenging task. The sludge that settles at the tank bottoms can become very thick and compact over time, making sludge removal difficult. This process is essential not only for recovering usable space but also for inspection and maintenance of the storage tanks themselves.
The approach to oily sludge treatment and removal from tanks must be systematic to ensure safety and efficiency. Specialized equipment is often required to break up and pump out the dense sludge. This process is often part of a larger shutdown or maintenance schedule for the facility.
Key steps in cleaning sludge from tanks include:
- Isolation and Preparation: The tank is taken out of service, emptied of any liquid oil, and safely isolated.
- Sludge Removal: Manual or automated systems are used to physically remove the sludge from the tank bottom.
- Initial Separation: The removed sludge may be pre-treated on-site to separate free oil and water.
- Final Cleaning and Inspection: The tank is thoroughly cleaned of any remaining residue and inspected for integrity before being returned to service.
Advanced Oil Sludge Drying Techniques
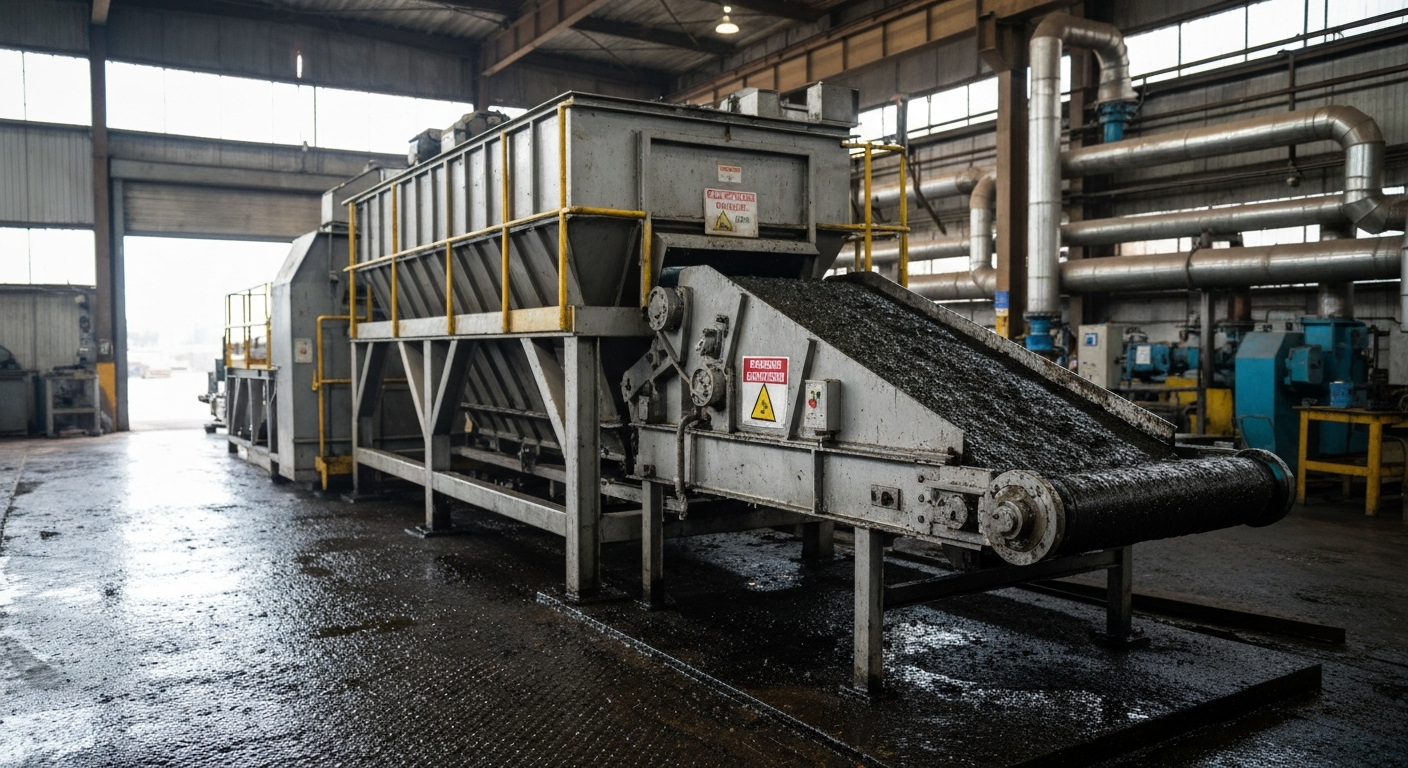

After initial separation, the remaining solid portion of the oil sludge still contains a significant amount of moisture and residual oil. Advanced drying techniques are a crucial treatment method used to further process this material. The primary goal of the drying process is to remove water, which dramatically reduces the sludge’s total volume and weight.
This reduction makes handling, transportation, and final disposal much more cost-effective. Thermal treatment is one of the most common and effective drying approaches. By applying heat, the moisture content is lowered, leaving behind a drier, more manageable solid product that can be evaluated for reuse. Let’s explore how these drying methods work.
Thermal Drying Methods and Their Effectiveness
Thermal drying is a highly effective process for treating oil sludge. It involves heating the sludge to evaporate the water content, leaving behind dried sludge and recovered oil. This method is particularly useful because it can reduce the final waste volume by up to 90%, significantly lowering disposal costs.
The drying process can be direct or indirect. Direct drying exposes the sludge to hot gases, while indirect drying heats the sludge through a heated surface without direct contact with flames. Indirect methods are often preferred as they can prevent the thermal degradation of valuable organic matter in the sludge.
The effectiveness of thermal drying is clear:
- Volume Reduction: Drastically lowers the amount of waste that needs to be transported and disposed of.
- Resource Recovery: Facilitates the separation and recovery of residual oil.
- Improved Handling: The resulting dried sludge is easier to store and handle than wet sludge.
- Pathogen Destruction: The high temperatures kill harmful bacteria, making the final product safer.
The Role of Modern Sludge Dryers in Oil Sludge Drying
Modern sludge dryers are at the forefront of efficient oil sludge treatment methods. These advanced machines are designed to optimize the drying process, ensuring uniform heat distribution and maximum moisture removal. Among the most innovative solutions is the Paddle Dryer, a technology that has revolutionized how industries handle oily sludge.
AS Engineers is a leading manufacturer of these highly efficient sludge dryers. Our Paddle Dryer uses rotating, heated paddles to agitate and indirectly heat the sludge. This continuous mixing ensures that the entire batch of sludge is dried evenly and thoroughly. This method is exceptionally good at reducing moisture content while using energy efficiently.
By using a state-of-the-art Paddle Dryer from AS Engineers, you can convert hazardous oily sludge into a dry, reusable material. This not only solves a difficult waste management problem but also aligns with sustainability goals by enabling resource recovery. Our solutions offer a compact and cost-effective way to manage your sludge treatment needs.
Safe and Sustainable Oil Sludge Disposal Methods
Once oil sludge has been treated and dewatered, the final step is its safe disposal or reuse. Choosing a sustainable disposal method is just as important as the treatment itself, as it determines the final environmental impact. The best approaches prioritize resource recovery and minimize the amount of waste sent to landfills.
Modern strategies for oily sludge focus on turning the treated solids into something useful. This could mean using it as an alternative fuel source or finding other industrial applications. The goal is to move away from simple disposal and toward a circular economy model. The following sections cover the most common disposal and reuse options available today.
Landfill, Incineration, and Reuse Options
After treatment, several disposal pathways are available for the remaining solid material. The chosen option often depends on the composition of the dried sludge and local regulations. Landfilling is a common choice, but it is becoming less favorable due to space limitations and the potential for long-term environmental liability.
A more sustainable option is incineration. When performed in a controlled environment, incinerating dried sludge can generate heat for energy recovery. This turns a waste product into a fuel source, reducing the need for fossil fuels. Another method is land farming, where sludge is spread on land and biodegraded by soil microorganisms, though this is only suitable for certain types of non-hazardous sludge.
Here are the primary options:
- Landfill: Disposing of the treated solids in a specially designed hazardous waste landfill.
- Incineration: Burning the sludge at high temperatures, often with energy recovery.
- Reuse as Fuel: Using the dried, hydrocarbon-rich solids as an alternative fuel in facilities like cement kilns.
- Construction Materials: In some cases, treated solids can be incorporated into materials like asphalt or bricks.

Regulatory Considerations and Best Practices in India
In India, the management of oil sludge is governed by strict environmental regulations under the Hazardous and Other Wastes (Management and Transboundary Movement) Rules. These rules classify oil sludge as a hazardous waste, mandating that industries follow specific guidelines for its collection, storage, treatment, and disposal. The Central Pollution Control Board (CPCB) sets the standards that all facilities must meet.
Adhering to these best practices is essential for compliance and environmental protection. This includes obtaining proper authorization for operating a sludge treatment facility, maintaining detailed records of waste generation and disposal, and ensuring that any third-party disposal company is properly certified. Failure to comply can result in significant penalties and legal consequences.
Reducing disposal costs while staying compliant is a key challenge. Investing in efficient treatment technologies, like advanced sludge dryers, helps reduce the final volume of hazardous waste. This not only lowers an organization’s environmental footprint but also makes compliance with India’s stringent environmental regulations more manageable and cost-effective.
Equipment Used in Oil Sludge Treatment Plants
An effective oil sludge treatment plant relies on a series of specialized pieces of equipment working together. Each machine plays a specific role in the overall waste management process, from initial separation to final drying. The combination of these treatment technologies determines the plant’s efficiency and its ability to recover valuable resources.
The selection of equipment depends on the type of oil sludge being processed and the desired outcome. Key machinery includes centrifuges for separation, reactors for chemical treatment, and dryers for moisture reduction. Let’s look at the specific technologies used for drying and processing, along with the necessary safety protocols.
Technologies for Oil Sludge Drying and Processing
A range of technologies is available for the drying and processing stages of oil sludge treatment. The goal of this equipment is to remove water, extract any remaining oil, and produce a solid material that is safe for disposal or reuse. The choice of technology impacts the overall efficiency and cost of the treatment plant.
One of the most critical pieces of equipment is the sludge dryer. These machines use thermal energy to evaporate water from the sludge. As a leader in this field, AS Engineers provides advanced Paddle Dryer systems that offer superior performance for this drying process. Other technologies, like centrifuges and decanters, are used for mechanical separation.
Common equipment found in treatment plants includes:
- Centrifuges: For separating solids, oil, and water based on density.
- Sludge Dryers: To thermally reduce moisture content, with the Paddle Dryer being a highly efficient option.
- Solvent Extraction Units: To chemically dissolve and recover oil from the solid sludge.
- Filtration Systems: For polishing the recovered water and oil.
Safety Measures and Operational Guidelines
Safety is paramount when operating an oil sludge treatment plant. Because oil sludge is a hazardous waste that often contains flammable hydrocarbons and toxic substances, strict safety measures must be in place to protect workers and the environment. These protocols cover everything from handling the raw sludge to operating the treatment equipment.
All personnel must be trained on the specific hazards associated with the treatment processes and equipped with appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE). Operational guidelines should clearly outline procedures for normal operation, emergency shutdowns, and spill response. Regular equipment maintenance is also a critical safety component, as it ensures everything runs correctly and prevents failures that could lead to accidents.
Implementing a robust safety management system is not just a regulatory requirement; it is essential for maintaining a safe workplace. This includes conducting regular risk assessments, safety drills, and continuous training. By prioritizing safety, you can ensure your treatment facility operates without incident and maintains full equipment efficiency.
Preventive Strategies for Oil Sludge Buildup
While advanced treatment solutions are effective, the best strategy for managing oil sludge is to prevent its formation in the first place. Proactive maintenance and monitoring can significantly reduce the rate of sludge accumulation in engines and storage tanks. This approach saves money on costly cleanups and extends the life of your equipment.
Implementing a program of regular inspections and early detection can help you identify potential issues before they become major problems. By addressing the root causes of sludge formation, you can maintain operational efficiency and minimize your waste generation. The following sections offer practical tips for prevention.
Maintenance Tips for Engines and Storage Tanks
Regular maintenance is the most effective way to prevent sludge formation in both engines and industrial storage tanks. For engines, this means adhering to a strict schedule for oil changes. Fresh engine oil contains detergents and dispersants that keep contaminants suspended, preventing them from settling and forming sludge in oil passages.
In the case of industrial storage tanks, periodic cleaning is essential. Even with the best practices, some sediment and water will inevitably settle over time. Scheduling regular tank cleanouts prevents this layer from becoming too thick and hard, making the process easier and less costly when it is time for a full-scale cleaning.
Follow these maintenance tips to minimize sludge buildup:
- Use High-Quality Engine Oil: Choose oils that meet or exceed manufacturer specifications for your engines.
- Follow Regular Oil Change Intervals: Do not extend oil change schedules, especially in severe operating conditions.
- Implement Tank Cleaning Schedules: Regularly inspect and clean storage tanks to remove accumulated sediment.
- Use Fuel and Oil Additives: Certain additives can help stabilize fuel and oil, reducing the tendency for sludge to form.
Monitoring and Early Detection Solutions
Beyond routine maintenance, modern monitoring solutions offer a powerful tool for the early detection of sludge formation. For engines, regular oil analysis can reveal signs of degradation and contamination long before sludge becomes a serious problem. This allows you to adjust maintenance intervals or identify underlying issues that contribute to poor engine performance.
In industrial settings, tank gauging systems can be used to monitor the level of sediment at the bottom of storage tanks. By tracking the rate of accumulation, you can plan for cleanouts more effectively and avoid unexpected capacity issues. These monitoring tools provide valuable data that helps shift your maintenance strategy from reactive to proactive.
Implementing a robust monitoring program gives you the insights needed to intervene early. This not only prevents catastrophic equipment failures but also optimizes your treatment processes by ensuring the sludge you do generate is managed before it becomes overly difficult to handle.
Conclusion
In summary, managing oil sludge effectively is crucial for both environmental sustainability and operational efficiency. By understanding the formation, implications, and treatment methods of oil sludge, industries can navigate the challenges associated with its disposal. Advanced drying techniques, particularly using modern sludge dryers, not only enhance the recycling of valuable materials but also comply with legal regulations. Implementing preventive strategies and adhering to best practices can significantly minimize sludge buildup and ensure safe disposal. As we continue to innovate in sludge treatment technologies, now is the time to adopt these methods for a cleaner and more efficient future. For a comprehensive solution tailored to your needs, consider exploring the offerings of AS Engineers, the leading manufacturer in sludge dryer technology.
Frequently Asked Questions
Is thermal drying the most effective way to reduce oil sludge volume?
Yes, thermal drying is a highly effective treatment method for oil sludge volume reduction. The drying process evaporates water, which can account for a large portion of the sludge’s mass. This significant reduction in volume makes transportation and disposal much more manageable and cost-effective.
What safety precautions are recommended during oil sludge treatment?
Key safety measures for oil sludge treatment include using proper personal protective equipment (PPE), ensuring adequate ventilation to prevent fume inhalation, and following strict operational guidelines. Since it’s a hazardous waste, all treatment processes must adhere to protocols for handling flammable and toxic materials.
How can industries benefit from advanced oil sludge treatment solutions?
Industries benefit by reducing their environmental impact, ensuring regulatory compliance, and lowering disposal costs. Advanced treatment technologies also allow for significant oil recovery and resource recovery from the waste stream, turning a liability into a valuable asset and improving overall operational sustainability.
Can you explain the process of drying oil sludge?
The drying process for oil sludge involves heating the material to remove its moisture content. Modern sludge dryers, such as a Paddle Dryer, use indirect heat to evaporate water efficiently. This treatment method reduces the sludge’s volume and weight, preparing it for safe disposal or reuse.
What are the most effective methods for oil sludge treatment?
The most effective treatment processes for oil sludge often involve a multi-step approach. This typically includes mechanical separation followed by advanced methods like thermal treatment or drying. The best waste management strategy combines these treatments with sustainable disposal methods like incineration for energy recovery.
Are there any safety or regulatory considerations for oil sludge treatment?
Yes, oil sludge is classified as hazardous waste, so its treatment is governed by strict environmental regulations. Companies must follow specific rules for sludge disposal and implement safety measures to protect workers. These treatment processes require adherence to legal standards to avoid penalties and environmental harm.
Is thermal drying effective for reducing the volume of oil sludge?
Absolutely. Thermal drying is extremely effective for oil sludge volume reduction. By using heat to evaporate the moisture content, the drying process can decrease the total volume and weight of the sludge by up to 90%, making it far more economical to handle and dispose of.
What are the environmental impacts of improper oil sludge disposal?
Improper oil sludge disposal has severe environmental impacts. As a hazardous waste, it can contaminate soil and groundwater with toxic chemicals and heavy metals. This pollution harms ecosystems, poses risks to human health, and can render land and water sources unusable for years.
What equipment is commonly used in oil sludge treatment plants?
Common treatment equipment includes centrifuges for separation, reactors for chemical treatment, and sludge dryers for removing moisture. Advanced waste management plants may also use systems for solvent extraction or thermal desorption. A Paddle Dryer is a key piece of equipment for the efficient drying of oil sludge.




