Are you looking for a clear and practical guide on how to handle ETP sludge in a way that protects the environment and complies with strict regulations? You’re in the right place. In this in-depth article, we’ll explore the realities of effluent treatment plant (ETP) sludge—from why it poses a serious concern to proven strategies for safe and sustainable sludge disposal. By the end of this post, you’ll know exactly how to manage ETP sludge in a responsible manner while maintaining high operational efficiency. Let’s dive in.
Effluent Treatment Plants (ETPs) play a crucial role in filtering and cleaning industrial wastewater. Yet, despite the effectiveness of these systems, a byproduct remains: ETP sludge. This sludge often contains heavy metals, organic pollutants, and pathogens that can harm people, contribute to water pollution, and threaten local ecosystems if managed improperly. It can also put industrial facilities at risk of non-compliance with environmental regulations, which can lead to hefty fines or legal action.
Whether you’re a plant manager, an environmental consultant, or an industry stakeholder, you need solutions that are both cost-effective and sustainable, especially when it comes to obtaining raw materials. In the sections that follow, we’ll outline the fundamentals of ETP sludge disposal and highlight proven, real-world approaches to ensure compliance and public safety.
Understanding ETP Sludge
When industrial wastewater flows through an ETP, it undergoes multiple treatment stages for the treatment of wastewater—primary, secondary, and sometimes tertiary. Each stage aims to remove contaminants like suspended solids, organic matter, and various chemicals. As these contaminants settle out, they form a residual byproduct called sludge.
Key Components of ETP Sludge
- Heavy Metals: Commonly found in sludge from industries like textiles, leather processing, electroplating, and chemical manufacturing. Chromium, lead, and cadmium are typical culprits present in industrial effluent.
- Pathogens: Bacteria, viruses, or other microbes can remain active if the sludge comes from food processing or pharmaceutical wastewater.
- Organic Pollutants: If the facility handles dyes, paints, or solvents, the sludge may contain organic compounds that degrade slowly and can leach into soil and groundwater. The process of sludge digestion plays a crucial role in breaking down these pollutants effectively.
- Nutrients: In some cases, sludge contains beneficial nutrients such as nitrogen and phosphorus. While these can be helpful for agricultural use, high concentrations of metals or chemicals can negate this benefit.
Proper understanding of these components is essential for choosing the right disposal or treatment method. If the sludge is laden with harmful substances, it calls for more advanced techniques, such as thermal treatment or chemical stabilization.
Common Challenges in ETP Sludge Disposal
ETP sludge is not just an afterthought—it’s a major operational and environmental challenge. If you’ve ever asked yourself why disposing of sludge is so complicated, you’re not alone. Many industries grapple with the following issues:
1. High Moisture Content
ETP sludge typically contains a large amount of water, which makes it heavier and more difficult to transport. High moisture content can also increase treatment costs because you need specialized equipment to reduce water content before final disposal.
2. Volatile Organic Compounds (VOCs)
Some industrial processes yield sludge that contains VOCs. These compounds can pose risks to air quality if not treated properly. Inadequate handling can lead to unpleasant odors and potential health hazards for workers and nearby communities.
3. Toxicity and Hazardous Materials
Heavy metals and toxic chemicals in sludge can contaminate soil and groundwater if disposed of in a landfill without proper liners or treatment processes. This contamination can become an enormous liability for industries and local authorities.
4. Strict Legal Requirements
Local and international guidelines often demand specific methods of sludge management. Non-compliance isn’t just a matter of paying a fine—it can also tarnish an organization’s reputation and disrupt operations.
5. Disposal Costs
In many regions, landfill space is limited, and fees are rising. High disposal costs can strain budgets, making it tempting to cut corners. However, improper shortcuts can lead to much bigger expenses later, including potential cleanup costs, legal repercussions, and brand damage.
Understanding these challenges helps companies better plan for safe, cost-effective etp sludge disposal. The next step is staying on the right side of environmental laws by knowing exactly how to meet and exceed regulatory standards.


Complying with Environmental Regulations
Many industries face international and local legislation governing sludge disposal. Agencies such as the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) and the Central Pollution Control Board (CPCB) in India have strict guidelines on how to treat and dispose of hazardous waste. Regulations often specify permissible concentrations of heavy metals, disposal methods, and documentation requirements.
Key Compliance Steps
- Sludge Characterization: Perform chemical and biological testing to identify contaminants and their concentrations, focusing on the biological process at play.
- Select Appropriate Treatment: Choose methods that effectively reduce toxicity levels before final disposal, considering the biological process involved in each method.
- Regular Monitoring: Conduct periodic tests on treated sludge and the disposal site to ensure ongoing compliance with the relevant biological process standards.
- Documentation and Reporting: Maintain accurate records to demonstrate your facility’s compliance to authorities.
Staying compliant not only helps you avoid fines and penalties but also builds public trust. Communities are more likely to support facilities that demonstrate transparent and responsible waste management practices.
Objectives of Treating ETP Sludge
Effective treatment of ETP sludge serves multiple objectives critical for environmental sustainability and public health. One primary aim is to significantly reduce the volume of sludge, decreasing disposal challenges and facilitating efficient waste management while minimizing its environmental impact. Stabilizing organic materials within the sludge not only diminishes odors but also minimizes the risk of hazardous emissions. Additionally, transforming sludge into usable resources through processes like anaerobic digestion supports resource recovery, ensuring compliance with environmental regulations while promoting ecological balance and safeguarding water quality.
Reducing volume of sludge
Identifying ETP sludge requires an understanding of its complex composition, often originating from industrial wastewater treatment processes. Typically, this sludge contains high levels of organic matter, heavy metals, and toxic chemicals, which can pose significant health hazards if not managed properly. Various treatment methods, including chemical treatment and anaerobic digestion processes, are utilized to stabilize and reduce the volume of sludge. Effective sludge management not only mitigates environmental impact but also aligns with regulatory requirements, ensuring safe disposal and continued resource recovery.
Stabilising organic material and removing odour
ETP sludge is a complex mixture generated from various effluent treatment processes. This material often contains high concentrations of organic matter, suspended solids, and heavy metals, reflecting the nature of the industrial waste water it originates from. Understanding the characteristics of ETP sludge is essential for implementing effective treatment and management strategies. Various methods, including thermal treatment and biological processes, can be employed to stabilize and reduce this sludge, ultimately minimizing its environmental impact and enhancing resource recovery efforts.
Top Treatment Methods for ETP Sludge
Several proven treatments can reduce the risks posed by ETP sludge. Each method has its pros and cons, so your choice will depend on the type of industry you operate, the contaminants involved, and your budget constraints.
1. Dewatering and Drying
- Mechanical Dewatering: Techniques like filter presses or centrifuges significantly reduce sludge volume by removing water.
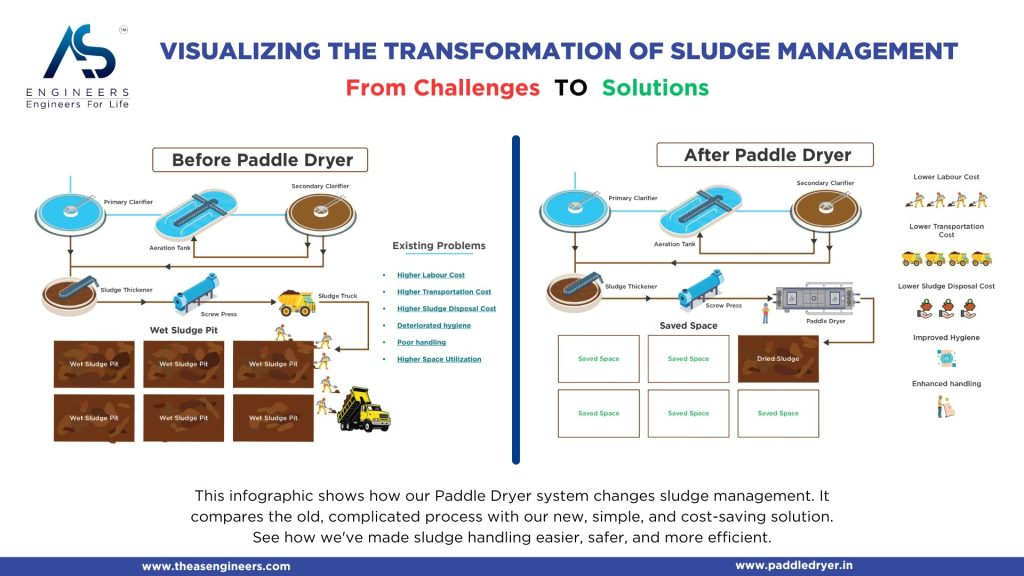
- Thermal Drying: Industrial dryers, such as paddle dryers or rotary dryers, reduce moisture to manageable levels, making sludge management more efficient.
2. Chemical Stabilization
Adding chemical agents like lime or other alkaline substances can neutralize acidic components in sludge and reduce pathogen survival rates. While it doesn’t entirely remove heavy metals, it can reduce odor and make the sludge safer to handle.
3. Incineration
High-temperature incineration destroys organic contaminants and significantly reduces sludge volume. However, this process can be expensive and may require sophisticated air pollution control equipment to capture harmful emissions.
4. Composting or Co-Composting
For sludge containing fewer toxic elements, composting can be a viable option. It involves mixing sludge with organic materials like sawdust or agricultural residues, leading to a stable product that can enhance soil fertility. Still, if heavy metals are present, composting must adhere to strict guidelines to avoid soil contamination.
5. Land Application
Land application involves spreading treated sludge over agricultural or forest land, primarily for nutrient benefits. This option is only suitable if the sludge meets specific quality standards, including low heavy metal content and pathogen levels.
6. Secure Landfilling
In cases where sludge is too toxic for reuse, a secure landfill with proper lining and leachate collection can be the safest choice. Although it’s a more passive approach, it’s often necessary when dealing with highly hazardous materials.
Each method comes with unique challenges and compliance requirements. Next, we’ll look at advanced strategies that combine several of these methods for maximum safety and efficiency.
Expert-Backed Strategies for Sustainable Sludge Management
Experts and environmental consultants often recommend a combination of methods rather than a single approach. Here are some strategies you can implement to make your ETP sludge disposal more sustainable and cost-effective.
1. Integrate Dewatering with Thermal Technologies
Combining mechanical dewatering (such as a filter press) with thermal drying solutions (like paddle dryers) can drastically lower sludge volume. This double-layered approach not only reduces disposal fees but also limits transportation costs because you’re dealing with a lighter, drier material.
2. Invest in Resource Recovery
Some facilities opt to recover valuable components from sludge, such as metals or energy. Through processes like pyrolysis or gasification, you can convert sludge into syngas or biochar, potentially offsetting disposal costs and reducing your carbon footprint.
3. Employ Real-Time Monitoring
Modern sensors and IoT-based monitoring systems can measure parameters like pH, moisture content, and chemical concentrations in real time. Continuous oversight ensures you can make immediate adjustments to maintain compliance and efficiency.
4. Partner with Certified Vendors
Working with third-party vendors or treatment facilities that specialize in etp sludge disposal can reduce your plant’s risk. Look for partners with a track record of compliance, transparent operations, and the necessary certifications.
5. Conduct Frequent Training
Your workers are on the front lines of sludge handling, so investing in regular training sessions goes a long way. Teach them proper safety measures, equipment operation, and early detection of potential issues. Engaged and knowledgeable staff can prevent accidents before they escalate.
6. Implement Closed-Loop Strategies
Where possible, adopt a circular model by reusing treated water in your processes. A closed-loop system can reduce wastewater volume, curb sludge production, and make your entire operation more sustainable.
By incorporating these expert-backed strategies, you set your facility on a path toward safer, more economical, and more environmentally friendly operations.
FAQs about ETP Sludge
1. What is ETP sludge, and why is it hazardous?
ETP sludge is the solid or semi-solid residue that remains after treating industrial wastewater in Effluent Treatment Plants. It can contain heavy metals, pathogens, and harmful chemicals, making it potentially hazardous to both the environment and human health if not managed properly.
2. How do I reduce the volume of ETP sludge?
You can use mechanical dewatering methods like filter presses, followed by thermal drying technologies such as paddle dryers. These processes significantly lower moisture content, thus reducing both the weight and volume of the sludge.
3. Is it possible to reuse or recycle ETP sludge?
In some cases, yes. Certain sludge can be composted for agricultural use or processed for energy recovery if it meets specific quality standards. However, sludge laden with heavy metals or toxic chemicals must undergo further treatment or be disposed of in secure landfills.
4. Which regulations apply to ETP sludge disposal?
Regulations vary depending on your region. In many countries, bodies like the U.S. EPA or the Central Pollution Control Board (CPCB) in India set guidelines on handling hazardous waste. Always perform thorough testing and maintain detailed records to show regulatory compliance.
5. What are some common mistakes in sludge management?
The most frequent errors include inadequate dewatering, ignoring chemical analyses, and improper landfill disposal without proper liners. Each misstep can increase risks of soil and groundwater contamination, potential legal liabilities, and harm to your company’s reputation.
6. What is ETP sludge and how is it generated in effluent treatment plants?
Sludge from effluent treatment plants embodies a complex mixture, derived primarily from the wastewater treatment process. Comprising organic matter and suspended solids, as well as sometimes heavy metals, ETP sludge presents significant challenges for waste management. The composition varies, influenced by factors such as the type of industrial effluent processed and the treatment methods employed, including those that maintain a high organic content.
With moisture content often high, effective sludge management strategies, including dewatering and chemical treatment, are vital to ensure safe disposal and minimize environmental impact while adhering to stringent environmental regulations.
7. What are the main challenges in disposing of ETP sludge?
In textile effluent treatment plants, the nature of ETP sludge comprises diverse organic and inorganic substances, heavily influenced by the type of industrial wastewater processed. Characterized by high moisture content, it often contains heavy metals and toxic chemicals, necessitating specialized treatment. The sludge management process involves multiple stages, including primary and secondary treatment, to minimize health hazards and environmental impact. Understanding the composition of ETP sludge allows for appropriate disposal methods, ensuring both public health protection and compliance with environmental regulations.
8. How can ETP sludge be utilized or recycled for profit?
Characterized by a complex composition, ETP sludge results from the treatment of industrial wastewater, primarily from effluent treatment plants. This sludge typically contains high levels of organic matter, suspended solids, and potential toxic contaminants such as heavy metals and volatile organic compounds.
Effective tertiary treatment of ETP sludge is essential to mitigate health hazards and environmental impact. Understanding its characteristics is crucial for implementing suitable sludge management and disposal methods, ensuring compliance with environmental regulations while promoting safe disposal practices.
9. What are the typical characteristics of ETP sludge from the textile industry?
ETP sludge, primarily generated from wastewater treatment processes, contains various organic and inorganic materials. Its composition often includes suspended solids, heavy metals, and volatile organic compounds, posing significant challenges for disposal. Effective ETP sludge management is crucial not only for compliance with environmental regulations but also for protecting public health.
The recycling of ETP sludge for use in building materials allows for safer disposal while effectively reducing the load of other building materials. Treatment options encompass biological processes like anaerobic digestion and chemical treatments involving substances like ferric chloride, ultimately aiming for safe disposal or resource recovery from the sludge.
10. What treatment solutions are available for managing ETP sludge effectively?
ETP sludge consists of residual materials generated during the treatment of industrial wastewater, particularly from effluent treatment plants. This sludge is characterized by high moisture content, organic pollutants, and sometimes hazardous substances like heavy metals and toxic chemicals.
The composition often includes suspended solids and organic matter, including textile sludge, necessitating further treatment to mitigate public health risks and environmental impact. Understanding these characteristics is critical for selecting appropriate sludge management strategies, including methods of stabilization and safe disposal to ensure compliance with environmental regulations.
11. Are there any standard operating procedures for handling and utilizing ETP sludge?
Effluent treatment plants generate ETP sludge as a byproduct of their wastewater treatment processes. This sludge typically contains high levels of moisture, organic matter, and various contaminants, including heavy metals and toxic chemicals. The composition of ETP sludge varies based on the type of industrial effluent processed, such as textile or paper waste. Understanding these characteristics is crucial for developing appropriate treatment and waste disposal methods, ensuring safe disposal, and minimizing the environmental impact associated with this waste material.
12. Can ETP sludge be used as fuel in recovery boilers?
The composition of ETP sludge varies significantly, containing organic matter, heavy metals, and toxic chemicals from industrial processes. Generated predominantly from wastewater treatment plants, this sludge often comprises suspended solids and organic pollutants, necessitating careful management.
Treatment plants generally focus on reducing moisture content to facilitate effective sludge disposal and enhance resource recovery. With the increasing emphasis on environmental protection, understanding the characteristics of this sludge is crucial for implementing safe disposal methods and complying with stringent environmental regulations, ensuring the safe disposal of harmful materials.
13. How is ETP sludge used as a partial replacement for cement in concrete?
ETP sludge primarily consists of residual solids generated during the wastewater treatment process. It often contains a mixture of organic matter, suspended solids, and various toxins, reflecting the pollutants present in the influent. Understanding its unique characteristics, including sewage sludge, is crucial for effective sludge management and treatment.
The moisture content is typically high, complicating disposal and treatment processes. Implementing appropriate sludge treatment options, including dewatering and thermal treatment, is essential for minimizing environmental impacts and ensuring compliance with stringent regulatory standards.
14. What are modern approaches to handling ETP sludge?
Understanding the intricate composition of ETP sludge is crucial for effective waste management. This byproduct of effluent treatment plants typically contains high levels of organic matter, suspended solids, and potentially hazardous pollutants. The sludge often exhibits elevated moisture content, complicating disposal and treatment processes. Moreover, identifying the presence of heavy metals and toxic chemicals necessitates rigorous analysis to ensure compliance with environmental regulations. Comprehensive analysis and secondary treatment methodologies, including chemical treatment and anaerobic digestion, ultimately enhance the safety and sustainability of final disposal practices.
15. What is the process for managing ETP sludge in the pulp and paper industry?
Characterized by a complex composition, the residue from wastewater treatment plants’ effluent treatment often contains a mixture of heavy metals, organic matter, and suspended solids. The presence of toxic chemicals poses significant health hazards, necessitating a precise understanding of its characteristics for effective sludge management. Various treatment processes are deployed, including anaerobic digestion and chemical stabilization, to reduce moisture content and enhance safety for final disposal. Properly treated sludge can benefit water pollution control efforts and meet stringent environmental regulations while maximizing resource recovery opportunities.
16. Is ETP sludge a hazardous waste?
Significant insights into ETP sludge reveal its complex characteristics arising from various industrial processes. Primarily generated during the treatment of wastewater, this byproduct contains high moisture content along with organic pollutants and heavy metals. The treatment plants engage in multiple stages, including primary sludge and secondary treatment, to mitigate the environmental impacts of ETP sludge. Understanding its composition, such as suspended solids and chemical constituents, is essential for developing effective disposal methods and ensuring compliance with environmental regulations.
17. What is ETP in wastewater?
Understanding the complexities of ETP sludge begins with recognizing its composition, which includes residual organic matter, heavy metals, and various contaminants from industrial processes. The treatment process typically involves multiple stages, such as primary, secondary, and activated sludge process tertiary treatment. These phases aim to reduce harmful pollutants and ensure that the final product meets environmental regulations. Effective sludge management not only minimizes health hazards but also enhances resource recovery options, paving the way for sustainable practices in wastewater treatment plants.
18. How to reduce sludge in ETP?
An insightful exploration of ETP sludge reveals its characteristics as a byproduct of wastewater treatment processes in sewage treatment plants. Generated primarily in effluent treatment plants, this sludge comprises suspended solids and organic matter, reflecting the composition of the industrial wastewater it processes.
Variability in moisture content and organic pollutants can complicate its management, necessitating careful treatment and disposal strategies. Understanding these characteristics is crucial for effective sludge management, ensuring compliance with environmental regulations, and safeguarding public health in the long term.
19. How long will activated sludge live without oxygen?
A thorough comprehension of ETP sludge thickening is essential for effective management in wastewater treatment processes. This sludge, a byproduct of effluent treatment plants, contains a mixture of organic materials, suspended solids, and toxic chemicals. Its characteristics, including high moisture content and the presence of heavy metals, pose significant challenges in disposal and treatment.
Proper understanding aids in implementing optimal treatment methods such as anaerobic digestion or chemical stabilization, ensuring safe disposal and minimizing environmental impact while promoting resource recovery in modern waste management practices.
20. Why is ETP sludge drying important?
In effluent treatment plants, the generation of sludge is inevitable due to the removal of suspended solids and organic contaminants during the wastewater treatment processes, including sludge treatment. The distinct characteristics of ETP sludge often include high moisture content and variations in organic matter, making it a challenge for safe disposal. Treatment options such as chemical stabilization and anaerobic digestion can mitigate the environmental impact. Understanding these foundational elements is crucial for developing effective sludge management strategies that align with environmental regulations and promote resource recovery.
21. What is the work of an effluent treatment plant?
ETP sludge comprises a heterogeneous mixture of organic matter, suspended solids, and toxic chemicals resulting from the wastewater treatment process in effluent treatment plants. Characteristically dense with high moisture content, it poses challenges for effective disposal. The presence of heavy metals and hazardous waste compounds can create significant health hazards and environmental impacts. Successful management often requires a combination of primary treatment, secondary, and tertiary treatment methods to stabilize sludge, reduce volume, and mitigate risks associated with disposal and final product use.
22. How do I reduce the volume of ETP sludge?
ETP sludge, primarily produced from wastewater treatment, contains a complex mixture of organic matter, suspended solids, and various contaminants. This sludge’s characteristics can vary significantly based on the type of waste being treated, including heavy metals and toxic chemicals, depending on the industrial source.
Effective biological treatment and sludge management strategies are integral for reducing its environmental impact, ensuring public health safety, and complying with stringent environmental regulations. Understanding the composition of ETP sludge is key to implementing effective treatment processes and disposal methods.
23. What’s your experience with ETP sludge disposal and sludge management?
ETP sludge consists of a complex mixture of organic and inorganic materials, emerging from the treatment of industrial wastewater at water treatment plants. This byproduct often contains high moisture content, heavy metals, and toxic chemicals, necessitating careful management. Understanding its composition is vital for effective treatment, as it directly influences disposal methods and environmental impact.
Innovative treatment processes, including anaerobic digestion and thermal treatment, help stabilize organic matter, reduce volume, and ultimately ensure safe disposal while contributing to resource recovery initiatives.
Conclusion: Taking Action on ETP Sludge
ETP sludge can pose a severe threat to the environment and human health if managed without care. By implementing advanced sludge management strategies—like combining mechanical dewatering with thermal drying, investing in resource recovery, and staying vigilant with real-time monitoring—you can turn this waste byproduct into a more manageable material. These actions not only keep you on the right side of environmental regulations but also help streamline operational costs.
It’s now your turn to take meaningful steps. Evaluate your current sludge management plan, consult with experts, and explore technologies that match your facility’s needs. Small improvements can make a major difference in reducing risks and protecting our planet.
What’s your experience with ETP sludge disposal and sludge management? Share your insights in the comments below! If you found this guide helpful, don’t forget to check out our related resources for more tips on staying compliant and environmentally responsible.




